
 MI-07375
MI-07375
1999
Western Flower Thrips Feeding Scars and Tospovirus Lesions on Petunia Indicator Plants
Michael J. McDonough,
Graduate Student Department of Horticulture
Daniel Gerace,
Research Fellow Department of Entomology
Mark E. Ascerno,
Extension Entomologist and Department Head Department of Entomology

© 2006 Regents of the University of Minnesota. All rights reserved.
 |
Lesions on petunia leaves caused by the feeding of western flower thrips (WFT).
- The white lesions on the right leaf are caused by WFT that are not carrying the tospovirus.
- The dark lesions on the left leaf are caused by WFT that are carrying the tospovirus.
|
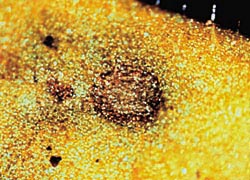 |
A closer look at a tospovirus lesion as it first appears on the petunia leaf. |
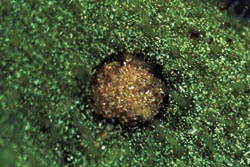 |
An older lesion on a petunia leaf. As the lesion ages, its center changes from black to tan. |
| From, Robb, K. L., C. Casey, A. Whitfield, and L. Campbell. 1998. A new weapon to fight INSV and TSVW. Grower Talks 61(12): 63-73. Photographs by Jack Kelly Clark; used with permission. |
Table 1. Host plants for tospoviruses TSWV and INSV listed by greenhouse crop type.
|
| |
TSWV |
INSV |
| Bedding Plants |
| Begonia |
+ |
+ |
| Blue daisy |
+ |
|
| Browallia |
|
+ |
| Caladium |
|
+ |
| Celosia |
|
+ |
| Coleus |
|
+ |
| Dahlia |
+ |
+ |
| Dusty miller |
|
+ |
| Eggplant |
+ |
+ |
| Fuschia |
+ |
|
| Gazania |
+ |
+ |
| Geranium |
+ |
+ |
| Gomphrena |
|
+ |
| Impatiens |
+ |
+ |
| Lobelia |
+ |
+ |
| Maltese cross |
|
+ |
| Marigold |
|
+ |
| Moss rose |
+ |
+ |
| Nasturtium |
|
+ |
| New Guinea Impatiens |
|
+ |
| Petunia |
+ |
+ |
| Phlox |
|
+ |
| Salvia |
+ |
+ |
| Sea lavender |
+ |
|
| Star of Bethlehem |
+ |
|
| Stock |
|
+ |
| Strawflower |
+ |
+ |
| Swan River daisy |
|
|
| Verbena |
|
+ |
| Zinnia |
|
+ |
| Foliage plants |
| Arrowhead vine |
|
+ |
| Bird's Nest fern |
|
|
| Chinese evergreen |
+ |
+ |
| Cordyline |
+ |
+ |
| Dieffenbachia |
+ |
|
| Dracaena |
+ |
+ |
| Japanese aralia |
+ |
|
| Kalanchoe |
+ |
+ |
| Maranta |
+ |
+ |
| Oleander |
+ |
|
| Pedilanthus |
|
+ |
| Piggyback plant |
|
+ |
| Pothos |
|
+ |
| Rubber tree |
+ |
+ |
| Schefflera |
|
+ |
| Swedish Ivy |
|
+ |
| Tradescantia |
|
+ |
|
| |
TSWV |
INSV |
| Weeping fig |
+ |
|
| Zebra plant |
|
+ |
| Non-Ornamentals |
| Broadbean |
+ |
|
| Celery |
+ |
|
| Endive |
+ |
|
| Garden bean |
+ |
|
| Lettuce |
+ |
|
| Pepper |
+ |
+ |
| Spinach |
+ |
+ |
| Tarragon |
|
+ |
| Tomato |
+ |
+ |
| African violet |
+ |
+ |
| Alstromeria |
+ |
+ |
| Amazon lily |
|
+ |
| Amaryllis |
+ |
+ |
| Anemone |
|
+ |
| Anthurium |
+ |
+ |
| Ardisia |
+ |
+ |
| Asiatic lily |
+ |
+ |
| Bromelia |
+ |
|
| Calceolaria |
|
+ |
| Calla lily |
+ |
|
| Chrysanthemum |
+ |
+ |
| Clivia |
+ |
|
| Cyclamen |
+ |
+ |
| Eucharis |
+ |
|
| Exacum |
|
+ |
| Florist's cineraria |
+ |
|
| Gardenia |
+ |
+ |
| Gerbera |
+ |
+ |
| Gladiola |
+ |
+ |
| Gloxinia |
+ |
+ |
| Hoya |
|
+ |
| Hydrangea |
+ |
+ |
| Lantana |
+ |
|
| Lipstick plant |
|
+ |
| Lisianthus |
+ |
+ |
| Mother of thousands |
|
+ |
| Oncidium |
+ |
|
| Oxalis |
|
+ |
| Peace lily |
+ |
|
| Peperomia |
+ |
+ |
| Phalaenopsis |
+ |
|
| Primula |
+ |
+ |
| Rain daisy |
+ |
|
| Ranunculus |
+ |
+ |
|
| |
TSWV |
INSV |
| Rhododendron |
+ |
|
| Ruscus |
|
+ |
| Schizanthus |
+ |
+ |
| Snapdragon |
|
+ |
| Statice |
+ |
|
| Stephanotis |
+ |
+ |
| Streptocarpus |
+ |
+ |
| Thanksgiving cactus |
|
+ |
| Perennials |
| Ajuga |
|
+ |
| Aster |
+ |
|
| Barberry |
|
+ |
| Bee balm |
|
+ |
| Bishop's weed |
|
+ |
| Black-eyed susan |
|
+ |
| Campanula |
|
+ |
| Catnip |
|
+ |
| Columnea |
+ |
+ |
| Delphinium |
|
+ |
| English daisy |
|
+ |
| Forget-me-not |
|
+ |
| Foxglove |
|
+ |
| Gaillardia |
+ |
|
| Gentian |
|
+ |
| Hosta |
|
+ |
| Osteospermum |
+ |
|
| Pentstemon |
|
+ |
| Peony |
|
+ |
| Physostegia |
|
+ |
| Polemonium |
|
+ |
| Poppy |
|
+ |
| Red Valerian |
+ |
+ |
| Sedum |
|
+ |
| Shasta daisy |
|
+ |
| Turtlehead |
|
+ |
| Veronica |
|
+ |
| Vinca |
+ |
+ |
| Weeds |
| Bittercress |
|
+ |
| Chickweed |
|
+ |
| Dandelion |
+ |
|
| Field bindweed |
+ |
|
| Galinsoga |
|
+ |
| Horseweed |
+ |
|
| Jewelweed |
|
+ |
| Lamb's quarters |
+ |
|


 Produced by Communication and Educational Technology Services, University of
Minnesota Extension Service.
Produced by Communication and Educational Technology Services, University of
Minnesota Extension Service.
In accordance with the Americans with Disabilities Act, this material is available in alternative formats upon request. Please contact your University of Minnesota Extension Service office or the Distribution Center at (800) 876-8636.
The University of Minnesota Extension Service is committed to the policy that all persons shall have equal access to its programs, facilities, and employment without regard to race, color, creed, religion, national origin, sex, age, marital status, disability, public assistance status, veteran status, or sexual orientation.
 MI-07375
MI-07375![]()
 MI-07375
MI-07375![]()




![]()
![]() Produced by Communication and Educational Technology Services, University of
Minnesota Extension Service.
Produced by Communication and Educational Technology Services, University of
Minnesota Extension Service.