 AG-MI-07448-GO
AG-MI-07448-GORevised 5/2000
![]()
 AG-MI-07448-GO
AG-MI-07448-GO
Revised 5/2000
![]()

INCREASE HABITAT FOR WILDLIFENative plants provide food for native wildlife such as birds, butterflies, bees, and beneficial insects that help control insect pests |

REDUCE YOUR LAWN MAINTENANCENative plants are adapted to the local environment and need less watering and fertilizing. Practice integrated pest management (IPM) and use fewer chemicals for a healthier land and environment |

PROTECT WATER QUALITYA vegetated buffer along your lakeshore helps to filter out pollutants and sediment before they enter the lake. Aquatic plants are especially efficient at trapping nutrients before they pollute the waterways |

BEAUTIFY YOUR PROPERTYNative plants along the water's edge create a more attractive view. Add meandering walkways and sitting benches to enjoy the landscape. |
Natural shorelands are delicate ecosystems critical to the health of Minnesota's 10,000 lakesYou can create a more natural shoreland through the process of native revegetation or landscaping with native plants. Choosing the right plants for you back yard helps to restore plant communities, creating diverse habitat for wildlife. Natural shorelands give us privacy, enhance our property values, control erosion, improve water quality and fish habitat, and increase native plant and animal diversity. |
| UPLAND | WET PRARIE | EMERGENT | SUBMERGENT |
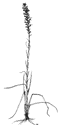 Liatris species blazing star |
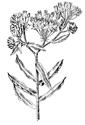 Asclepias incarnata swamp milkweed |
 Alisma plantago-aquatic water plantain |
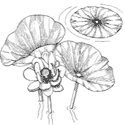 Nelumbo lutea American lotus |
 Enchinacea angustifolia purple coneflower |
 Carex comosa bottlebrush sedge |
Pontederia cordata pickerelweed |
 Vallisneria americana wild celery |
 Andropogon gerardii big bluestem |
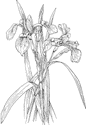 Iris versicolor blue flag iris |
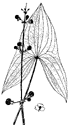 Sagittaria latifolia arrowhead |
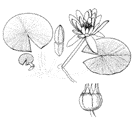 Nymphaea odorata white water-lily |
 Monarda fistulosa wild bergamot |
Juncus effusus soft rush |
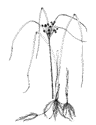 Scripus species bulrush |
|
 Ratibida pinnata gray-headed coneflower |
Lobelia cardinalis cardinal flower |
Typha latifolia cattail |
|
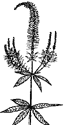 Veronicastrum virginicum Culver's root |
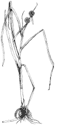 Sparganium americanums bur-reed |
|
For More Information Websites: CUES, Center for Urban Ecology and Sustainability, www.entomology.umn.edu/cues MN DNR, Minnesota Department of Natural Resources, www.dnr.state.mn.us University of Minnesota Extension Serviec, www.extension.umn.edu Funding: Metropolitan Council of the Twin Cities Area, Gervais Lake Shoreland Project Cooperators: Gervais Lake Association; Ramsey-Washington Metro Watershed District; Department of Entomology, University of Minnesota; Minnesota Department of Natural Resources; University of Minnesota Extension Service |
Plant species vary by region. Consult an expert for final determination. Transplanting aquatic species to DNR protected waters requires a DNR permit.


![]()
Produced by Communication and Educational Technology Services, University of Minnesota Extension Service.
In accordance with the Americans with Disabilities Act, this material is available in alternative formats upon request. Please contact your University of Minnesota Extension Service office or the Distribution Center at (800) 876-8636.
The University of Minnesota Extension Service is committed to the policy that all persons shall have equal access to its programs, facilities, and employment without regard to race, color, creed, religion, national origin, sex, age, marital status, disability, public assistance status, veteran status, or sexual orientation.