|
|
Back to Pest Identification and Diagnosis
 |
 |
|
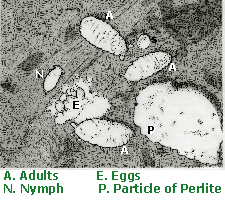
| Ground Mealybug Nymphs From: University of California |
Life Cycle |
| DESCRIPTION | |
|
Adult Females: The ground mealybug is white and 2.4 to 3.9 millimeters long. It resembles a springtail, but moves much more slowly and cannot jump. The ground mealybug has slender waxy filaments that form a sort of netting over some individuals. The ground mealybug also secretes a small amount of wax, which can give the soil a somewhat bluish appearance when the mealybugs are abundant. Pritchard's mealybug is snow white and 1.6 to 2.1 millimeters long and oval. It has small to non-existent eyes. |
|
| BIOLOGY | |
|
Host Plants: The ground mealybug feeds on the roots of anemone, chrysanthemum, gladiolus, iris, and numerous other flowers, shrubs, and ornamental grasses. Pritchard's mealybug has become a serious pest of African violet, although it also infests
Achillea, Arctostaphylos, Geum, and Polygala.
Damage: At times the ground mealybug becomes abundant enough to damage its host. Pritchard's mealybug causes devitalization, foliage deterioration, and even death of its host plant. Life Cycle: Little has been published on the life history of root mealybugs. When infested African violets are irrigated, Pritchard's mealybugs crawl out of the drainage holes and spread throughout the greenhouse. Eggs are laid in a loose ovisac in clusters of at least six eggs. All stages can be found on the roots and potting mix of African violets where they resemble slow moving, snowy white collembola. |
|
| MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES | |
|
Pesticides: Pesticides applied as dips, drenches, or
granules are more effective for root mealybug control than are foliar sprays. For specific chemical control recommendations, consult the Cooperative Extension Service. |
Back to Pest Identification and Diagnosis
 |
(C) Regents of the University of
Minnesota. All rights reserved. |
 |
 |