|
|
Back to Pest Identification and Diagnosis
CUBAN LAUREL THRIPS
SCIENTIFIC NAME: Gynaikothrips ficorum (Marchal)
CLASS: Insecta
ORDER: Thysanoptera
FAMILY: Phlaeothripidae
 |
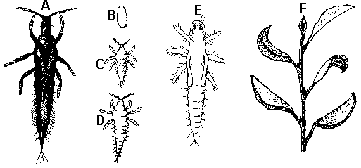 A. Adult B. Egg C-D. Larvae E. Pupa F. Damage to ornamental fig |
|
|
Adult Cuban Laurel Thrips From: University of Florida |
Life Cycle From: NC Extension |
| DESCRIPTION | |
|
Adults: Cuban laurel thrips are large thrips (2.6 to 3.6 mm) that are dark yellowish brown to black. Eggs: The eggs is cylindrical with rounded ends, smooth, and translucent white. Larvae: The first stage larva is a tiny, translucent white insect. In top view the first stage larva is almost oval. Second stage larvae are also translucent white but are similar to the adult in size and shape. Both instars have red eyes. The abdominal segments taper from the thorax. In top view the second stage larvae are shaped like an elongate diamond. The posterior tube becomes dark in older larvae and is held pointing up. Prepupae and Pupae: Prepupae are similar to second stage larvae except that the wing buds are externally visible. Pupae have longer wing buds and the antennae are folded back over the head. |
|
| BIOLOGY | |
|
Distribution: The Cuban laurel thrips is a pantropical species that occurs wherever
Ficus retusa is planted. It has been recorded outdoors in California, Texas, Hawaii, and Florida. Host Plants: Cuban laurel thrips feed on Indian laurel, weeping fig, India rubber plant, other figs, and various shrubs and herbs. In the floricultural industry, weeping fig is the host most often infested. Damage: This pest feeds on the tender, pale green leaves causing sunken, reddish to purplish spots along the midrib. Immature thrips cause the leaves to curl inward or fold into a pocket in which the thrips continue to develop and in which they lay eggs. Heavily infested leaves eventually become tough and brown or yellow. They eventually drop from the plant prematurely. Infested trees will not be killed, but the ornamental value of the plant is reduced markedly. Like the flower thrips, the Cuban laurel thrips also bites people. Life Cycle: Eggs are laid in great numbers inside the surface of the curled leaf. All stages of development can be found at any time within the pocket galls. Development from egg to egg-laying females takes about 30 days. Adult Cuban laurel thrips are active fliers and migrate rapidly during hot weather. |
|
| CONTROL | |
|
Because the Cuban laurel thrips only attacks the tender, new foliage on small plants, it should be possible to prune out the new growth and eliminate the thrips population. Consequently there is no suitable foliage for feeding and oviposition and the infestation should die out before new growth emerges. Two anthocorid bugs, Macrotracheliella laevis Champion and Cardiastethus rugicollis Champion, have been reported to be predators of the Cuban laurel thrips in Puerto Rico. Another anthocorid bug, Montandoniola moraguesi (Puton), was introduced from the Philippines in Hawaii to control this thrips. The insidious flower bug is a common predator of the Cuban laurel thrips in Florida. |
Back to Pest Identification and Diagnosis
 |
(C) Regents of the University of
Minnesota. All rights reserved. |
 |
 |