|
Cottonwood Leaf Beetle: Monitoring |
The cottonwood leaf beetle, Chrysomela scripta F., can be a major
defoliator in young poplar plantations. Defoliation (Fig. 1) can result in
height and diameter decreases as well as increased lateral branching and
terminal forking which will significantly reduce biomass of cottonwoods used
for pulp and biofuels.
Research is underway to develop a sustainable management system that relies
on multiple tactics to manage cottonwood leaf beetle in poplar plantations.
Current management utilizes the broad-spectrum insecticide, Sevin, which
honey producers believe is causing loss of foraging bees and hives. In
addition, Sevin will kill foraging lady beetles which feed on cottonwood
leaf beetle eggs. We are studying whether other pesticides can kill
cottonwood leaf beetles and conserve lady beetles.
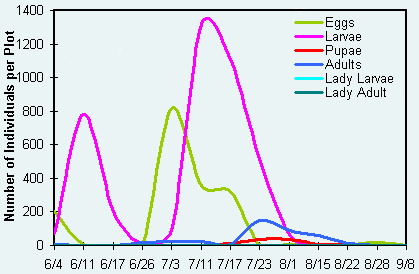
A field survey was done during 2002 in four poplar plantations near
Alexandria, MN to count the number of cottonwood leaf beetles (Figs. 2 and
3) and predatory lady beetles. We are studying whether lady beetles,
Coleomegilla maculata and Harmonia axyridis, can manage
cottonwood leaf beetle populations. We are developing degree-day
calculations to associate beetle activity with accumulated heat units for
better pesticide application timing (Table 1). |
|
Figure 1
 |
Figure 2
 |
|
Figure 3
|
Table 1
|
Gen. 1 |
Gen. 2 |
Gen. 3 |
|
Site |
Date |
DD |
Date |
DD |
Date |
DD |
| 1 |
June 4 |
109 |
July 20 |
617 |
Aug. 15 |
977 |
| 2 |
June 4 |
109 |
|
|
Aug. 7 |
793 |
| 3 |
|
|
July 10 |
495 |
Aug. 15 |
867 |
| 4 |
June 4 |
109 |
July 10 |
495 |
Aug. 28 |
977 |
|
|
|
Date |
|
|
Benefits |
- We will develop alternative and sustainable management plans for
cottonwood leaf beetle.
- These tactics will offer more sustainable long-term control of the
beetle and reduce conventional pesticide use.
|
|
Future Aims |
-
Evaluate alternative pesticides for management
of cottonwood leaf beetle. Determine if these pesticides are captured in
the flavonoid pinocembrum, the residue on Populus leaves that bees use for
propolis.
- Determine if the entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana can
increase overwintering mortality.
- Determine whether release of Harmonia axyridis, Asian lady beetle, or
Coleomegilla maculata, twelve spotted lady beetle, will significantly
reduce egg numbers.
|


